Robot-Human Collaboration: The Future of Assembly?
Manufacturing and assembly processes are complex, multifactorial activities that demand a lot of resources, planning and monitoring throughout their implementation. The devil is in the details, and even small errors can result in much greater unwanted outcomes.
Traditionally, assembly and production processes were manual tasks done by human labor. With the advancement of technology, more and more solutions started to emerge to support the productivity, safety and efficiency of these activities.
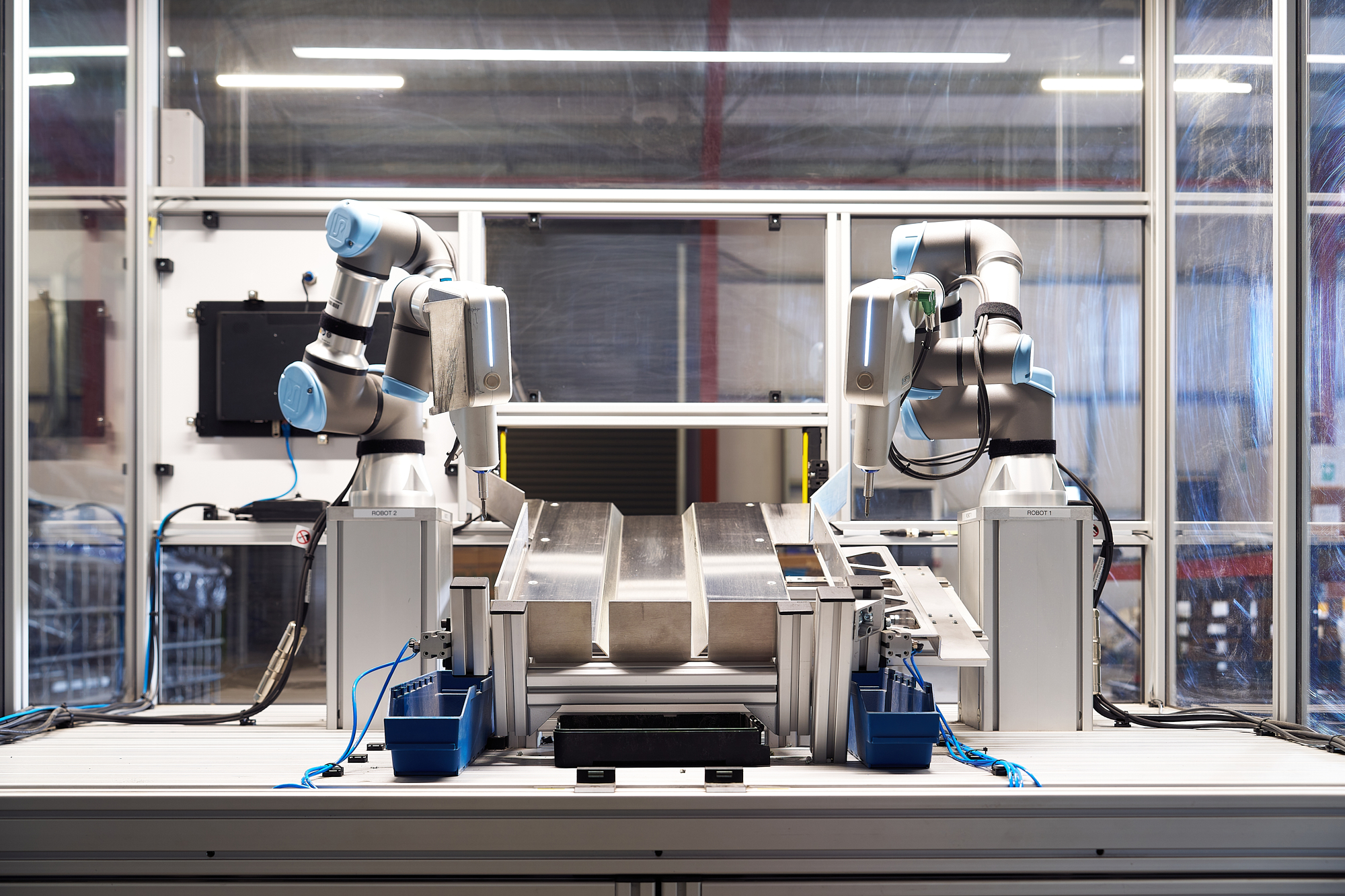
Robotics have been a major step ahead in the automatization of assembly tasks, such as screwdriving. Yet, the automation of production initially meant that robots could only perform specific tasks, most separated from the human workforce, which although provided tremendous benefits for manufacturers, still did not come without its own limitations. These solutions often required complex programming with the involvement of external experts to work properly, and reconfiguration took long durations out of the production workflow.
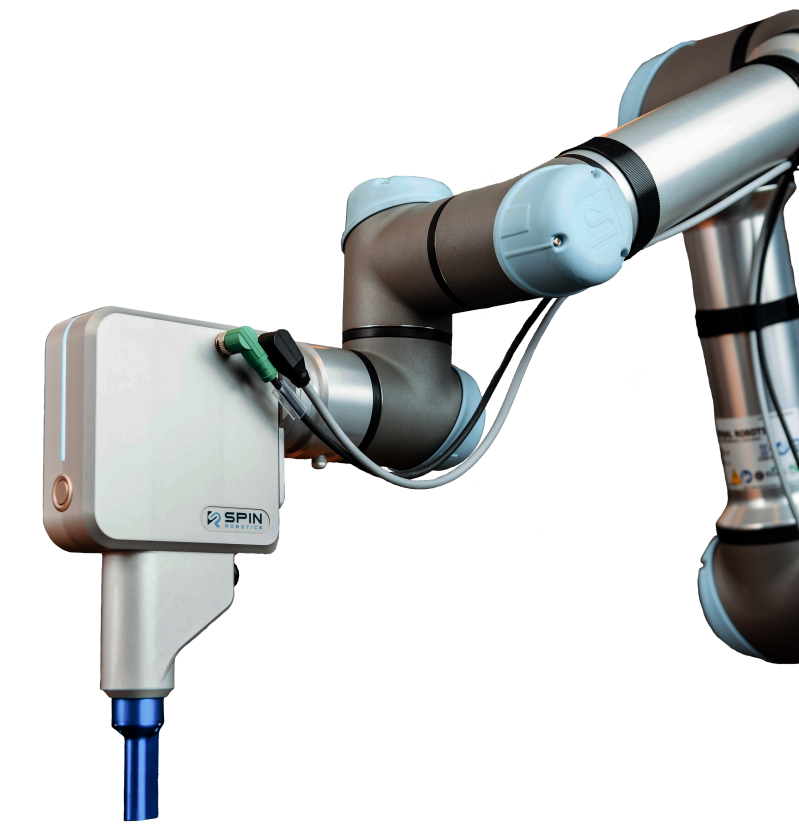
A new subset of robots, also known as ‘collaborative robots (or cobots) was designed specifically - as the name suggests - to collaborate with the human workforce. These robots provide much more flexibility in the assembly processes, increase safety in the workspace while keeping humans away from hazardous and dangerous tasks, such as screwdriving. At the same time by being able to take over more tasks from people and by supporting their activities directly, these people can be switched to more fulfilling, value-adding activities that are better served by humans. A classic win-win situation for everyone.
We might wonder how can assembly processes as specific as screwdriving can leverage the use of collaborative solutions? Screwdriving as an activity is one of the most strenuous and repetitive activities on the assembly lines that can benefit the most out of the application of collaborative robots on the shop floors. Screwdriving, however, is a multivariate task, which requires operators to keep many metrics in mind during the process, such as torque, screw capacity, size, the material used, and more.
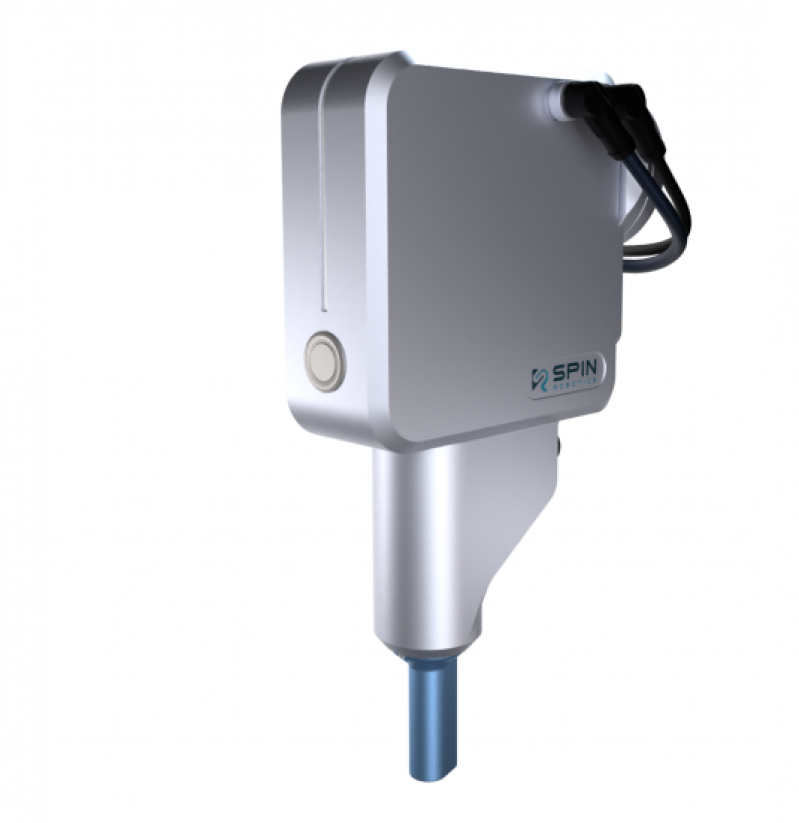
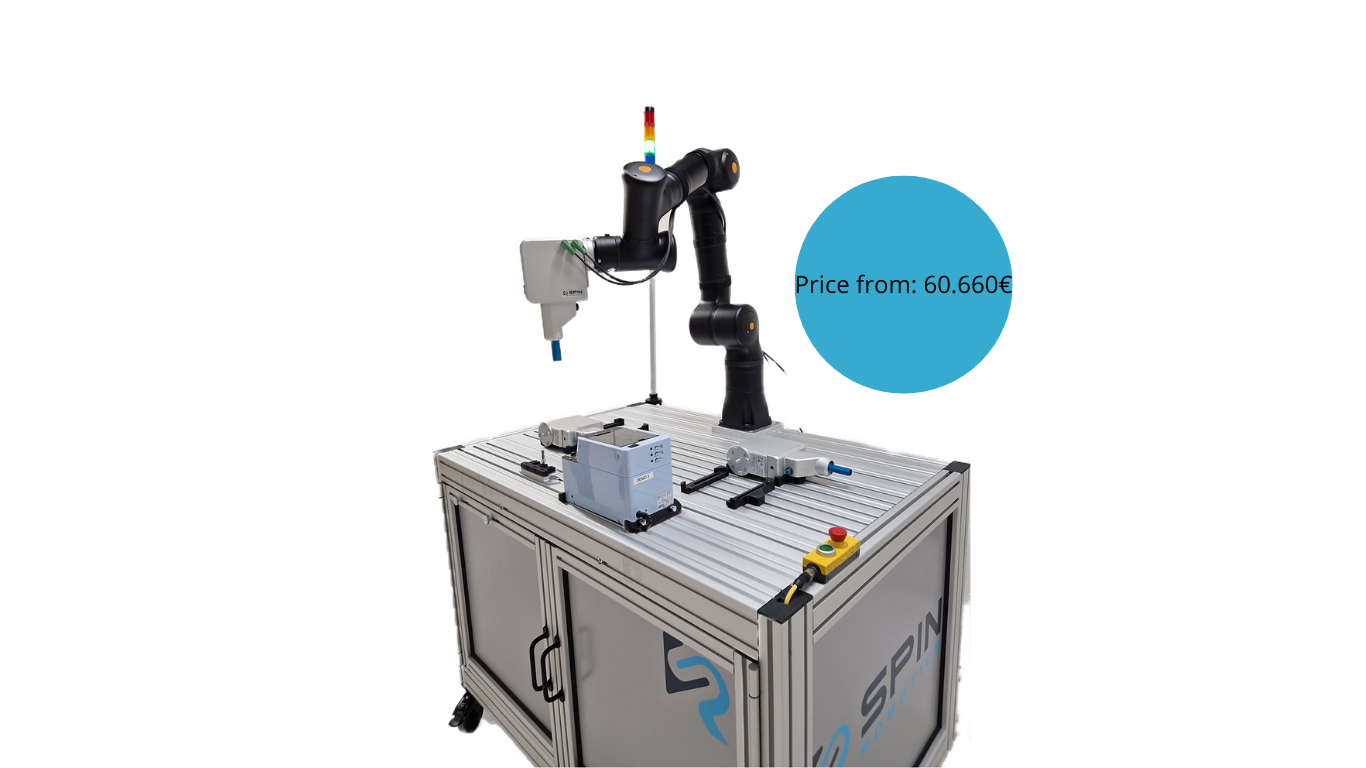
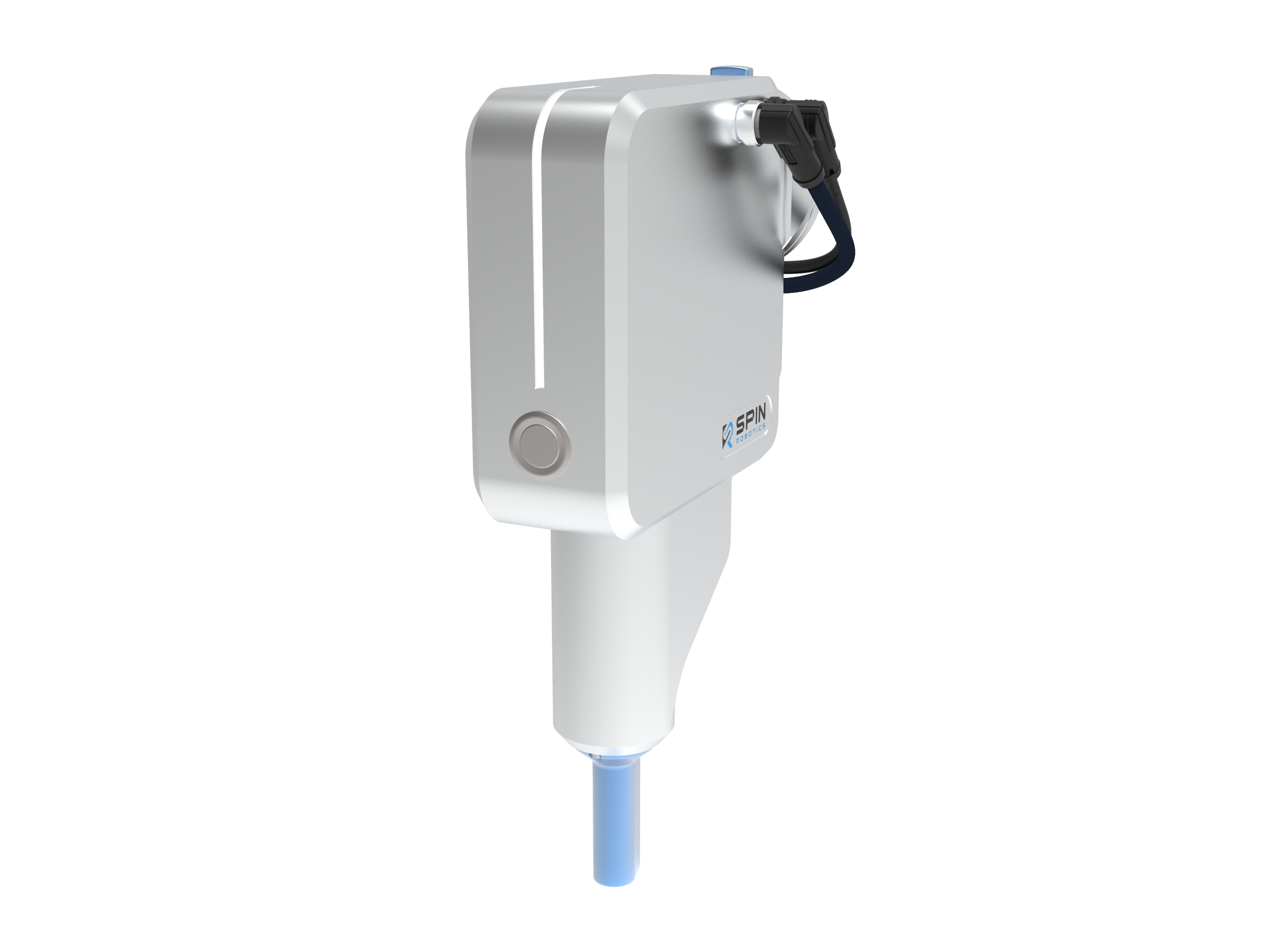
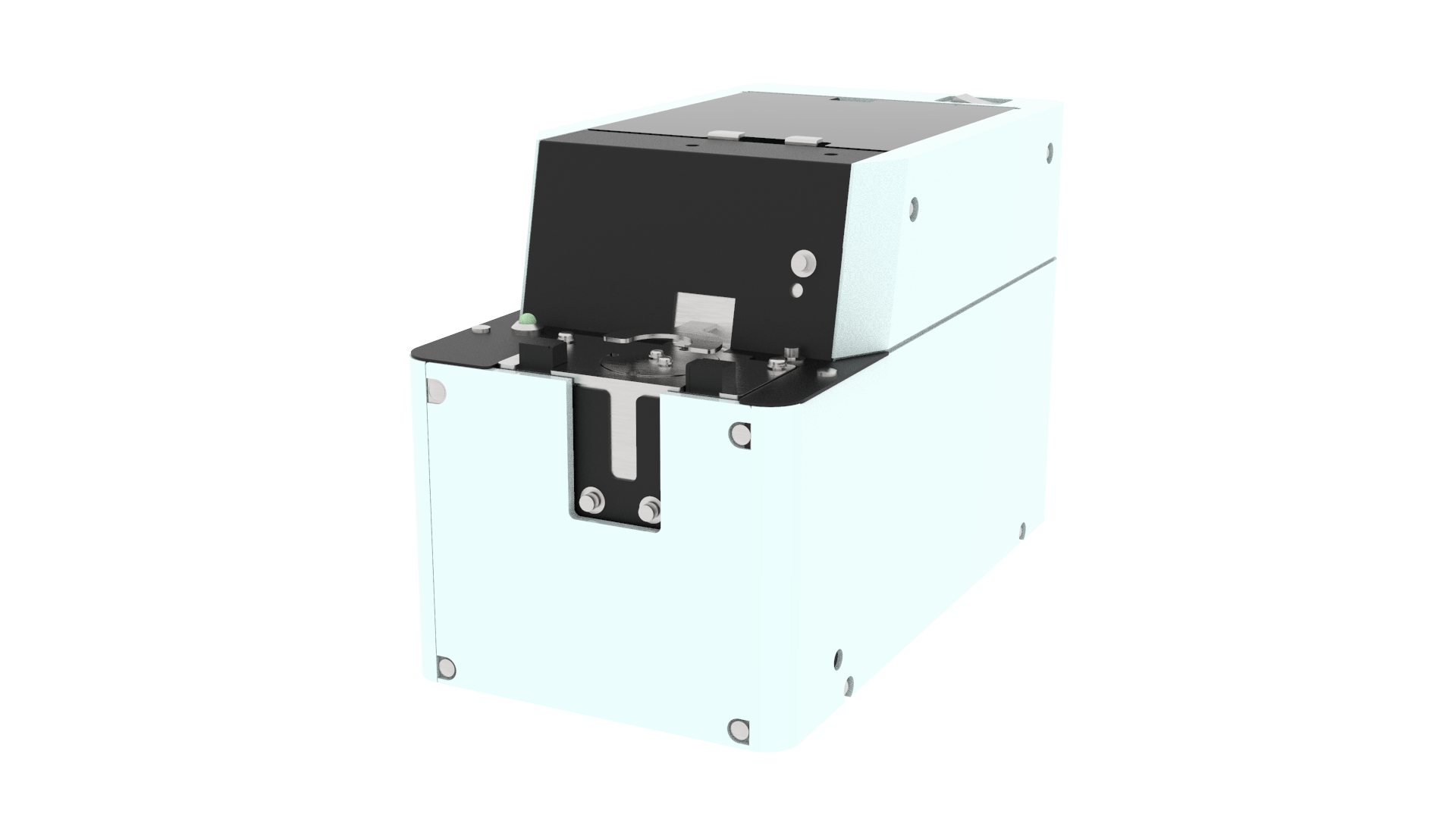
The screwdriver tools (SD35/SD70) developed by us at Spin Robotics were designed specifically to support the human-robot collaboration throughout the assembly processes. Our ISO-certified solution enables manufacturers to facilitate the productivity and efficiency of their production lines. Moreover, it creates a safe and flexible work environment, where people can work around robots without having to worry about getting injured.
The screwdriver tools essentially allow manufacturers to adopt a way of collaboration between humans and robots, that will most probably be a fundamental practice in the future of assembly. Manufacturers that adapt these solutions to their repertoire early will be able to get a big step ahead of other players on the market.
Are interested in learning more about our Screwdriver Tools? Check out our product page or contact us for more information.