How to set up the work environment for cobots in assembly
Finding the right screwdriver application isn’t always a clear-cut decision for manufacturers.
While advances in automation have made it easier for companies to access, and use robotic screwdriver solutions, often these can come with their own challenges. Additionally, to needing extensive planning before installation, longer reconfiguration, relatively higher investment costs, and less flexibility, robots need to be integrated into an environment where machines should be able to work safely, and effectively alongside human employees.
Collaborative robots (Cobots) can provide the benefits of traditional automated screwdriver solutions, with the additional “collaboration” component, which makes these robots safe around employees, and invaluable for assembly lines.
According to a recent report by Statzon, the global cobot market is currently valued at around 1.3 billion USD. The growing trend is expected to continue in the future with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of +37.8% until 2028.
“Collaborative robots represent the fast-growing industrial robotics market. Cobots currently account for around 5% of industrial robot sales. Technological advancements have made the applications of cobots a reality in many manufacturing industries.”
Within cobot applications, screwdriver solutions currently have an approximate market share of 3%. As there is a constantly growing need to automate complex manufacturing processes that require high accuracy and precision, screwdriver applications are expected to experience a further increase in demand, along with other tasks where cobots can provide significant benefits to companies.
Moreover, a variety of market trends are expected to further-facilitate the steep growth rate of the cobot market. These drivers include:
• A growing demand for robotics and automation.
• Low investment costs and high return on Investments (ROI).
• The broad applicability of cobots.
• Increasing interest and support from governments.
• Digital transformation, and the use of disruptive technologies, such as 5G, IoT, Artificial Intelligence, Industry 4.0.
Before investing in any screwdriver solution, companies should first investigate their specific needs, opportunities, and resources, to make sure that their work environment will be able to utilize cobots efficiently.
Among other aspects, the following key steps should be made to prepare for the implementation of cobot-enhanced screwdriver systems:
1. Select tasks that can be outsourced with the help of cobots.
Cobot and humans can work alongside providing a better and more productive work environment. Repetitive tasks can indeed be replace by cobots, but in another hand the work efficiency relies on the collaboration of man plus machine resulting in a higher productivity output.
2. Set up the workspace
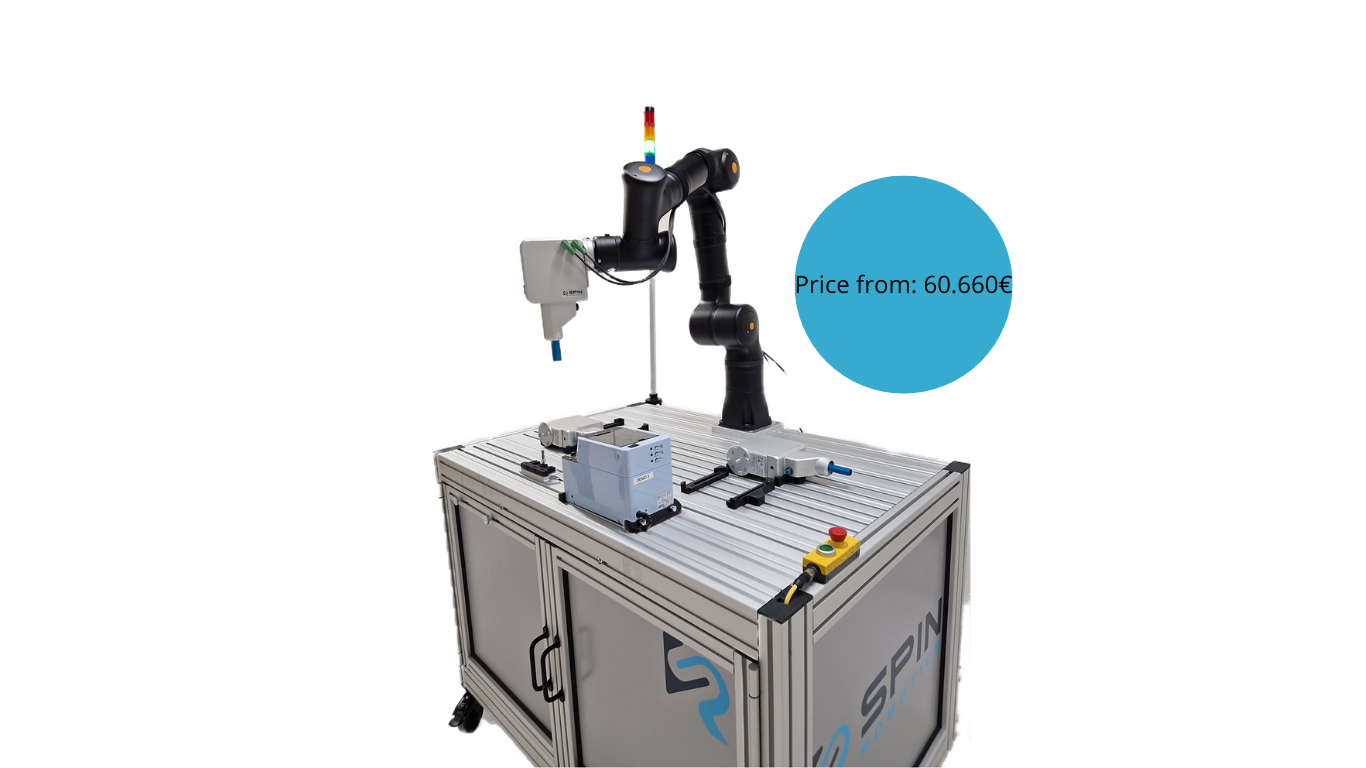
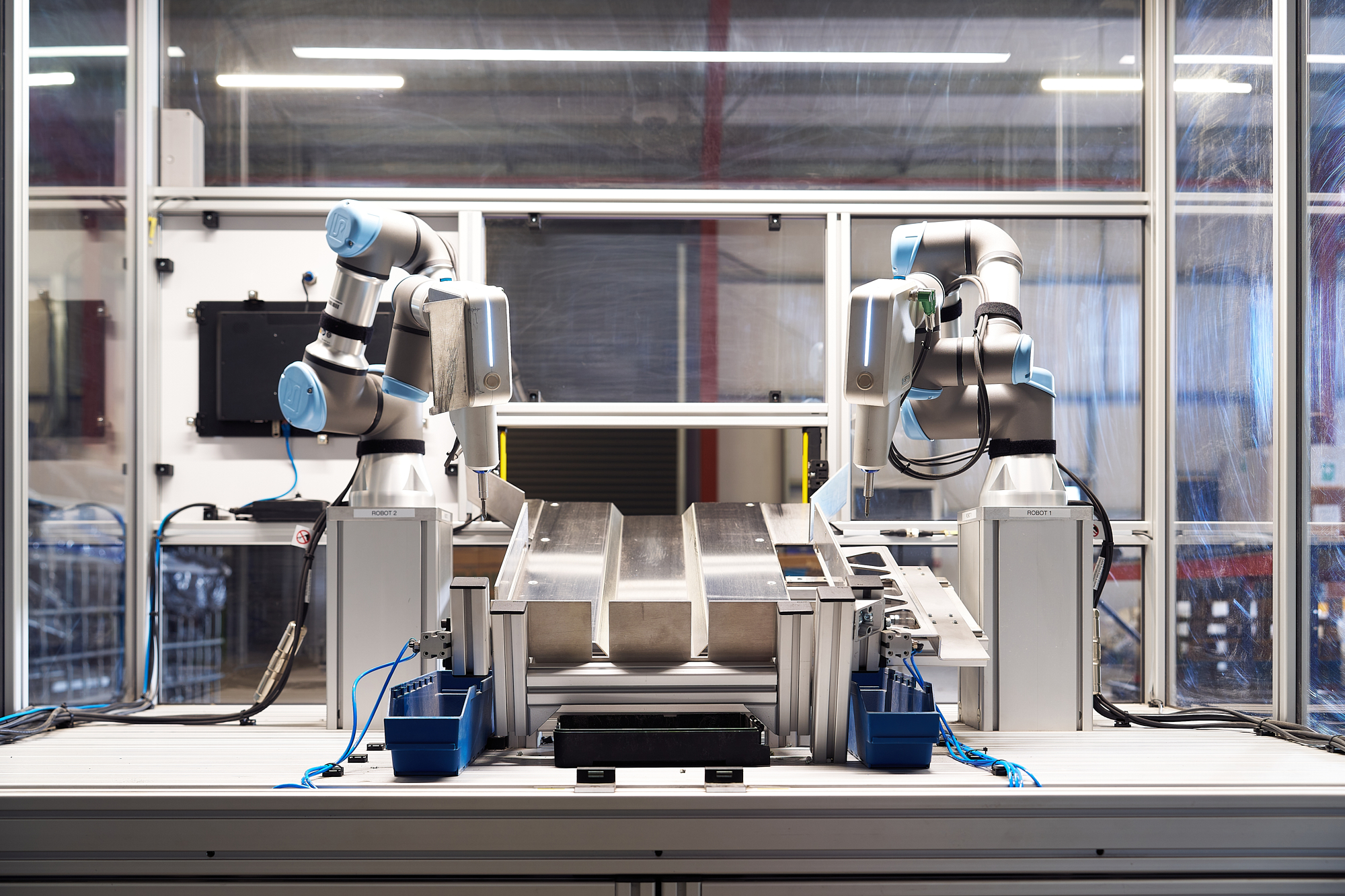
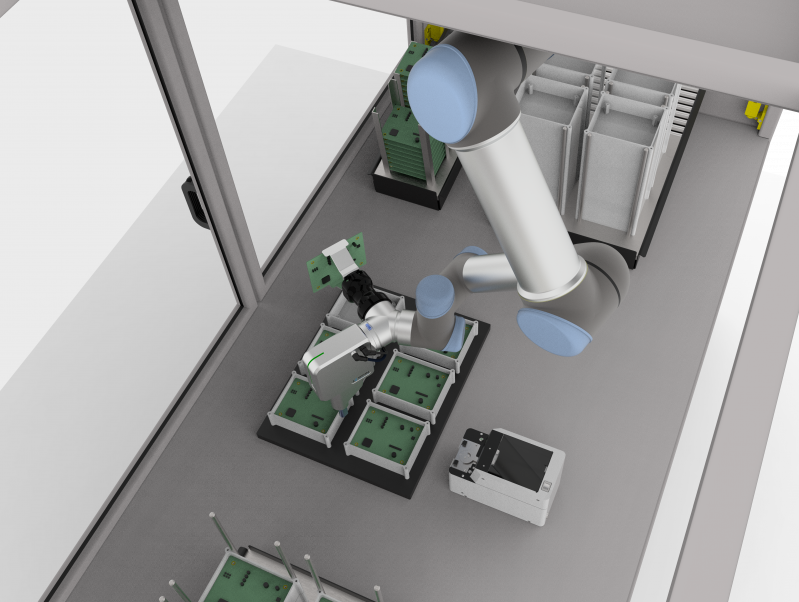
After identifying a work opportunity for a cobot, manufacturers should consider the working environment that will have to be set up around the machine. Companies need to decide on the needed cobot cell, its location, setup, and how employees could interact with the cobots.
These considerations are essential to evaluate not only the feasibility of the implementation process, but also highlight the need for any further safety considerations.
3. Use intelligent intuitive components to easy the initial risk assessment process
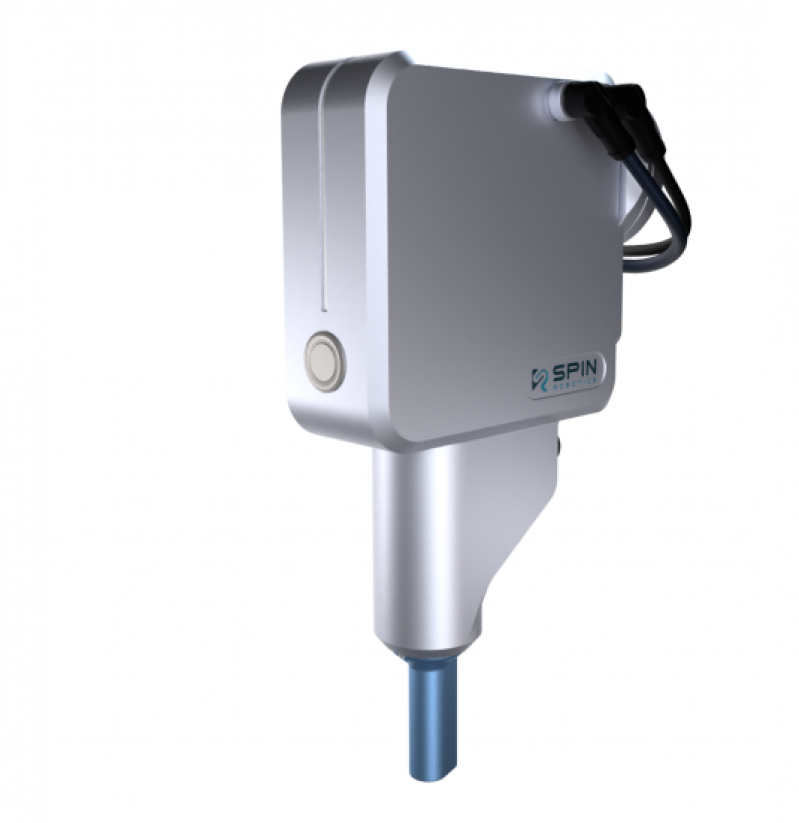
Although setting up cobots for screwdriving applications can be done with internal expertise, Spin Robotics’ smart tool and software enable smooth risk assessment when the automation process starts at the factory floor. Therefore, resulting in a safe work environment for employees by minimize the risks around usability.
4. Maintain caution, and monitor performance
The importance of providing the proper training to all employees on the shop floors, on how to operate, interact with, and work safely alongside cobots, while constantly monitoring the performance of the screwdriver process is hard to not overemphasize.
Learn more about our easy-to-use, Intelligent Plug'n'Produce screwdriver tooling designed specifically to be used by cobots.